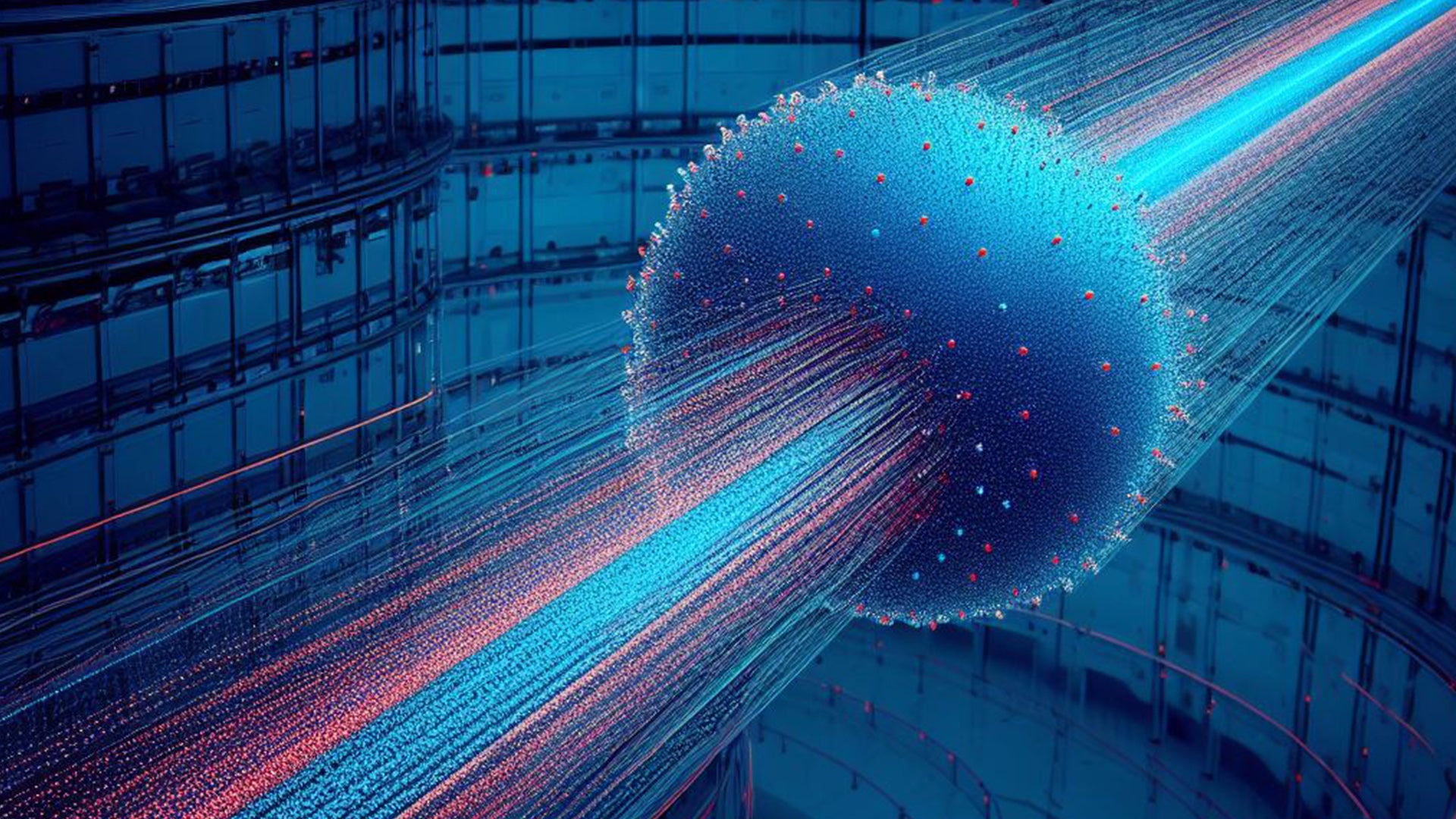
Muons: Revolutionizing Geo-Location Tracking
In today's fast-paced world, the need for accurate and reliable geo-location tracking is more critical than ever. From navigating city streets to tracking wildlife migrations, monitoring environmental changes, and even pinpointing underground resources, precise location data is indispensable. While Global Positioning System (GPS) technology has been a game-changer, it does have its limitations. However, a new player in the field, muon-based tracking, has emerged as a promising solution. Muons are subatomic particles that have the potential to revolutionize geo-location tracking. In this blog, we will explore what muons are, how they work, and their potential to shape the future of geo-location tracking.
Understanding Muons:
Muon particles, often referred to simply as muons, are elementary particles in the same family as electrons. These subatomic particles are created when high-energy cosmic rays collide with the Earth's atmosphere, producing a shower of secondary particles, including muons. Muons are charged and decay relatively quickly, with a half-life of just 2.2 microseconds, but they possess a unique property that makes them an intriguing candidate for geo-location tracking: they can penetrate all types of materials, including water and even solid structures such as buildings and the Earth's crust, without being affected.
How Muon-Based Tracking Works:
Muon-based tracking relies on the ability of muons to penetrate various materials and their interactions with those materials. The basic principle involves measuring the rate at which muons pass through a given substance. This rate is influenced by the density of the material. High-density materials, such as metals or concrete, slow down muons more than low-density materials like air or soil. By tracking the flux of muons as they travel through an object, it is possible to create a 3D map of its density.
Muon detectors are used to capture and record muon interactions with an object or environment. These detectors are placed strategically around the area to be tracked, similar to how GPS satellites are positioned in space. The data collected from these detectors is then processed to create a detailed map of the object's internal structure or the geological features below the Earth's surface. This method offers an unprecedented level of accuracy and detail compared to conventional geophysical techniques.
Advantages Over GPS:
Muon-based geo-location tracking offers several advantages over traditional GPS technology:
- Penetration of All Materials: Unlike GPS, which can be blocked by physical obstacles or interference, muons can penetrate all materials without disruption. This means that they can be used to track objects or locations deep underground, within buildings, or underwater.
- Immune to Interference: GPS signals can be jammed or tampered with, making them vulnerable to disruptions. Muons, on the other hand, are not susceptible to such interference, enhancing the reliability of geo-location data.
- Improved Precision: Muon-based tracking provides incredibly precise data, allowing for highly detailed 3D imaging of objects or geological structures. This makes it invaluable for applications such as underground resource exploration, archaeological surveys, and environmental monitoring.
Future Applications:
Muon-based geo-location tracking holds immense potential across various fields. Some potential applications include:
- Underground Resource Exploration: Muons can help accurately map the distribution of valuable resources like minerals, oil, and natural gas deep underground, reducing the cost and environmental impact of mining operations.
- Archaeological Surveys: Muon tracking can be used to explore archaeological sites without the need for excavation, preserving historical artifacts and sites.
- Environmental Monitoring: Monitoring changes in geological structures and underground water reservoirs can aid in understanding and addressing environmental challenges, such as land subsidence and groundwater depletion.
- Homeland Security: Muon detectors can be deployed to scan cargo containers and identify hidden contraband or dangerous materials, enhancing border security.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Muons can help assess the structural integrity of buildings and bridges without invasive methods, ensuring public safety.
Muon-based geo-location tracking is poised to transform the way we gather location data. Its ability to penetrate all materials and immunity to interference make it a robust and versatile technology. As research and development in this field continue, we can expect a host of exciting applications and improvements that will revolutionize underground exploration, infrastructure inspection, and much more. While GPS has been an incredible tool for geo-location, the emergence of muon-based tracking represents the next step in the evolution of location-based technologies, promising a more accurate and reliable future for geo-location tracking.
Also in News

Why OHANA Exists? The Future of Connection, Trust, and Sustainability
OHANA is a movement to rebuild how the world connects - securely, sustainably, and together. Because when we connect People and Planet through technology built on trust, we create not just networks… We create OHANA - a family that spans the world.

Why Strong Terrestrial Communication Still Matters.
The ionosphere is a crucial layer of Earth's upper atmosphere, extending from about 50 km to 1,000 km above Earth’s surface. It plays a critical role in both our natural environment & modern technological systems. While often overlooked, the ionosphere serves as a shield, a signal reflector, and a space weather regulator, influencing everything from global communications to climate patterns.